| [1]Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281-297.
[2]Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V,et al. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell.1993;75(5):843-854.
[3]Wightman B, Ha I, Ruvkun G. Posttranscriptional regulation of the heterochronic gene lin-14 by lin-4 mediates temporal pattern formation in C. elegans. Cell. 1993;75(5):855-862.
[4]Kozomara A, Griffiths-Jones S. miRBase: integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res.2011;39(Database issue): D152-D157.
[5]Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2009;10(2):126-139.
[6]Fabian MR, Sonenberg N, Filipowicz W.Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 2010;79:351-379.
[7]Thomas M, Lieberman J, Lal A. Desperately seeking microRNA targets. Nat Struct Mol Biol.2010;17(10): 1169-1174.
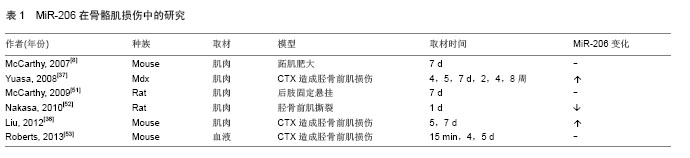
[8]Mccarthy JJ, Esser KA. MicroRNA-1 and microRNA-133a expression are decreased during skeletal muscle hypertrophy. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007;102(1):306-313.
[9]Mccarthy JJ, Esser KA, Andrade FH.MicroRNA-206 is overexpressed in the diaphragm but not the hindlimb muscle of mdx mouse. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;293(1): C451-C457.
[10]Small E M, O'Rourke J R, Moresi V, et al. Regulation of PI3-kinase/Akt signaling by muscle-enriched microRNA-486. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(9):4218-4223.
[11]van Rooij E, Liu N, Olson EN. MicroRNAs flex their muscles. Trends Genet. 2008; 24(4):159-166.
[12]Callis TE, Deng Z, Chen JF, et al. Muscling through the microRNA world. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2008;233(2): 131-138.
[13]Cifuentes D, Xue H,Taylor DW,et al.A novel miRNA processing pathway independent of Dicer requires Argonaute2 catalytic activity. Science.2010;328(5986): 1694-1698.
[14]Mccarthy JJ. MicroRNA-206: the skeletal muscle-specific myomiR. Biochim Biophys Acta.2008;1779(11):682-691.
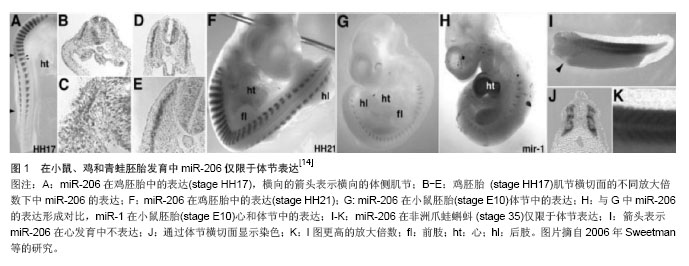
[15]Sweetman D, Rathjen T, Jefferson M, et al. FGF-4 signaling is involved in mir-206 expression in developing somites of chicken embryos. Dev Dyn.2006;235(8):2185-2191.
[16]Chen JF, Mandel EM, Thomson JM, et al. The role of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 in skeletal muscle proliferation and differentiation.Nat Genet.2006;38(2): 228-233.
[17]Sweetman D, Goljanek K, Rathjen T, et al.Specific requirements of MRFs for the expression of muscle specific microRNAs, miR-1, miR-206 and miR-133. Dev Biol. 2008; 321(2):491-499.
[18]Rao PK, Kumar RM, Farkhondeh M, et al. Myogenic factors that regulate expression of muscle-specific microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2006;103(23):8721-8726.
[19]Kim H K, Lee Y S, Sivaprasad U, et al. Muscle-specific microRNA miR-206 promotes muscle differentiation. J Cell Biol.2006;174(5):677-687.
[20]Winbanks CE, Wang B,Beyer C, et al.TGF-beta regulates miR-206 and miR-29 to control myogenic differentiation through regulation of HDAC4. J Biol Chem.2011; 286(16): 13805-13814.
[21]Anderson C, Catoe H, Werner R. MIR-206 regulates connexin43 expression during skeletal muscle development. Nucleic Acids Res.2006;34(20):5863-5871.
[22]Yan D, Dong XE, Chen X,et al.MicroRNA-1/206 targets c-Met and inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma development. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(43):29596-29604.
[23]Taulli R, Bersani F, Foglizzo V, et al. The muscle-specific microRNA miR-206 blocks human rhabdomyosarcoma growth in xenotransplanted mice by promoting myogenic differentiation. J Clin Invest.2009;119(8):2366-2378.
[24]Williams AH, Valdez G, Moresi V, et al.MicroRNA-206 delays ALS progression and promotes regeneration of neuromuscular synapses in mice. Science.2009; 326(5959): 1549-1554.
[25]Tang F, Kaneda M, O'Carroll D, et al.Maternal microRNAs are essential for mouse zygotic development. Genes Dev.2007; 21(6): 644-648.
[26]Dey BK, Gagan J, Dutta A. miR-206 and-486 induce myoblast differentiation by downregulating Pax7. Mol Cell Biol. 2011; 31(1):203-214.
[27]Cacchiarelli D, Martone J, Girardi E, et al. MicroRNAs involved in molecular circuitries relevant for the Duchenne muscular dystrophy pathogenesis are controlled by the dystrophin/nNOS pathway. Cell Metab.2010;12(4):341-351.
[28]Maciotta S, Meregalli M, Cassinelli L, et al. Hmgb3 is regulated by microRNA-206 during muscle regeneration. PLoS One.2012;7(8):e43464.
[29]Rosenberg MI, Georges SA, Asawachaicharn A, et al. MyoD inhibits Fstl1 and Utrn expression by inducing transcription of miR-206. J Cell Biol.2006;175(1):77-85.
[30]Liu H,Chen SE,Jin B,et al.TIMP3: a physiological regulator of adult myogenesis. J Cell Sci.2010;123(Pt 17):2914-2921.
[31]Bernstein E, Kim SY, Carmell MA, et al.Dicer is essential for mouse development. Nat Genet. 2003;35(3):215-217.
[32]Kanellopoulou C, Muljo SA, Kung AL, et al. Dicer-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells are defective in differentiation and centromeric silencing. Genes Dev.2005;19(4):489-501.
[33]Murchison EP, Stein P, Xuan Z, et al. Critical roles for Dicer in the female germline. Genes Dev.2007;21(6):682-693.
[34]Eisenberg I,Eran A,Nishino I,et al.Distinctive patterns of microRNA expression in primary muscular disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(43):17016-17021.
[35]Greco S, De Simone M, Colussi C, et al. Common micro-RNA signature in skeletal muscle damage and regeneration induced by Duchenne muscular dystrophy and acute ischemia. FASEB J. 2009;23(10):3335-3346.
[36]Liu N, Williams AH, Maxeiner JM, et al. microRNA-206 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration and delays progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mice. J Clin Invest.2012;122(6):2054-2065.
[37]Yuasa K, Hagiwara Y, Ando M, et al. MicroRNA-206 is highly expressed in newly formed muscle fibers: implications regarding potential for muscle regeneration and maturation in muscular dystrophy.Cell Struct Funct. 2008;33(2):163-169.
[38]Gambardella S, Rinaldi F, Lepore SM, et al. Overexpression of microRNA-206 in the skeletal muscle from myotonic dystrophy type 1 patients. J Transl Med. 2010;8:48.
[39]Liu W, Wen Y, Bi P, et al. Hypoxia promotes satellite cell self-renewal and enhances the efficiency of myoblast transplantation. Development. 2012;139(16):2857-2865.
[40]Macquarrie KL, Yao Z, Young JM, et al. miR-206 integrates multiple components of differentiation pathways to control the transition from growth to differentiation in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Skelet Muscle.2012;2(1):7.
[41]Missiaglia E, Shepherd CJ, Patel S, et al. MicroRNA-206 expression levels correlate with clinical behaviour of rhabdomyosarcomas. Br J Cancer. 2010;102(12):1769-1777.
[42]Miura P,Amirouche A,Clow C,et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression is repressed during myogenic differentiation by miR-206. J Neurochem. 2012;120(2):230-238.
[43]Valdez G, Heyer MP, Feng G, et al.The role of muscle microRNAs in repairing the neuromuscular junction. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e93140.
[44]Novak J, Kruzliak P, Bienertova-Vasku J, et al.MicroRNA-206: a promising theranostic marker. Theranostics. 2014;4(2): 119-133.
[45]Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS, et al. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature.2010;466(7308):835-840.
[46]Lehotzky A, Lau P, Tokesi N, et al.Tubulin polymerization- promoting protein (TPPP/p25) is critical for oligodendrocyte differentiation. Glia.2010;58(2):157-168.
[47]Westendorp B, Major JL, Nader M, et al.The E2F6 repressor activates gene expression in myocardium resulting in dilated cardiomyopathy. FASEB J. 2012;26(6):2569-2579.
[48]Hidaka H, Seki N, Yoshino H, et al. Tumor suppressive microRNA-1285 regulates novel molecular targets: aberrant expression and functional significance in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 2012;3(1):44-57.
[49]Chen X,Yan Q,Li S,et al. Expression of the tumor suppressor miR-206 is associated with cellular proliferative inhibition and impairs invasion in ERalpha-positive endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2012;314(1):41-53.
[50]Chen J F, Tao Y, Li J, et al. microRNA-1 and microRNA-206 regulate skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by repressing Pax7. J Cell Biol.2010;190(5): 867-879.
[51]Mccarthy JJ, Esser KA, Peterson CA, et al. Evidence of MyomiR network regulation of beta-myosin heavy chain gene expression during skeletal muscle atrophy. Physiol Genomics. 2009;39(3):219-226.
[52]Nakasa T,Ishikawa M, Shi M, et al. Acceleration of muscle regeneration by local injection of muscle-specific microRNAs in rat skeletal muscle injury model. J Cell Mol Med. 2010; 14(10):2495-2505.
[53]Roberts TC, Godfrey C, Mcclorey G, et al. Extracellular microRNAs are dynamic non-vesicular biomarkers of muscle turnover. Nucleic Acids Res.2013;41(20):9500-9513.
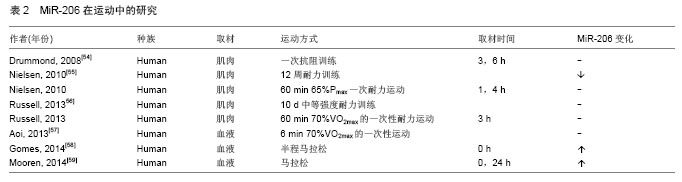
[54]Drummond MJ, Mccarthy JJ, Fry CS, et al. Aging differentially affects human skeletal muscle microRNA expression at rest and after an anabolic stimulus of resistance exercise and essential amino acids. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008; 295(6):E1333-E1340.
[55]Nielsen S, Scheele C, Yfanti C, et al.Muscle specific microRNAs are regulated by endurance exercise in human skeletal muscle.J Physiol.2010;588(Pt 20):4029-4037.
[56]Russell AP, Lamon S, Boon H, et al.Regulation of miRNAs in human skeletal muscle following acute endurance exercise and short-term endurance training. J Physiol. 2013;591(Pt 18): 4637-4653.
[57]Aoi W, Ichikawa H, Mune K, et al. Muscle-enriched microRNA miR-486 decreases in circulation in response to exercise in young men. Front Physiol.2013;4:80.
[58]Gomes C P, Oliveira-Jr G P, Madrid B, et al. Circulating miR-1, miR-133a, and miR-206 levels are increased after a half-marathon run. Biomarkers. 2014;19(7):585-589.
[59]Mooren FC, Viereck J, Kruger K,et al.Circulating microRNAs as potential biomarkers of aerobic exercise capacity. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2014; 306(4):H557-H563.
[60]Kroh EM, Parkin RK, Mitchell PS, et al.Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods.2010;50(4): 298-301. |